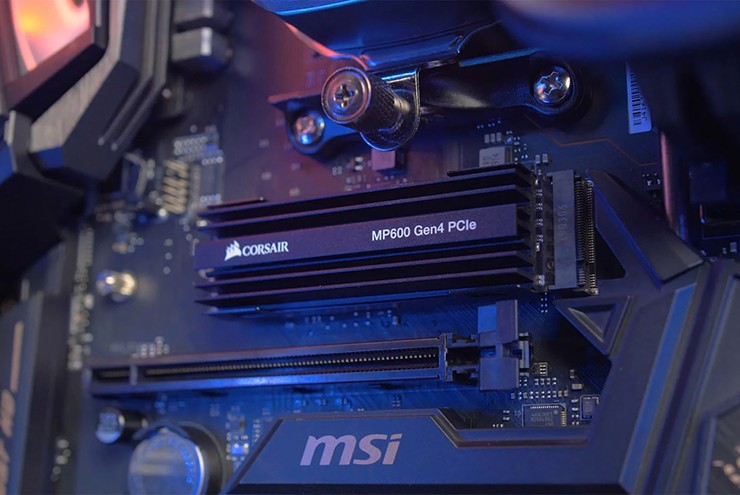
If you want to speed up your computer, you should consider using two SSDs instead of one if the motherboard on your device supports it.
There are two ways to take advantage of two SSDs on your computer. One is to configure the two drives in a RAID 0 array to combine the read and write speeds of both for impressive benchmark results. Another is to use one SSD for the operating system and the other for applications and games. Either way is useful for the following reasons.
Separate operating system and applications
RAID 0 is not necessarily recommended for improving computer speed because flash drives are already fast, so users will only see speed increases in benchmark results, not in everyday use. A much more effective way to improve performance with two SSDs is to separate the operating system and applications or data.
Many motherboards support a single SSD slot.
If you use one SSD for the operating system and a second SSD for applications and games, these processes will not compete for bandwidth, which is especially useful for those who need to edit videos or 3D models. Users can store the operating system and programs on one drive and the second drive for project files to avoid competing for bandwidth.
SSD Durability
Two SSDs offer better reliability than one SSD because there are many arguments about the durability of SSDs. This includes concerns about wear and tear, as well as SSDs being more durable than traditional hard drives (HDDs) due to the lack of mechanical parts.
Using two SSDs in a RAID 1 array is a great way to ensure users don't lose important data or experience downtime while performing important work.
Using two SSDs on your computer gives a good performance boost.
Separate write-intensive applications and drive encryption
Another way to improve reliability with two SSDs is to separate applications and data so that write-intensive applications run on the primary SSD. Media, video games, documents, and project files should be stored on the second SSD.
Finally, dual SSDs provide better data protection. By physically separating data, users can encrypt each drive separately.
If the primary drive fails due to a faulty update or other operating system issue, the user can safely erase the data from the primary drive.


